In terms of politics, capitalism is a socio-economic system that is based on private ownership of resources or capital. In terms of economy, capitalism becomes an economic system that is also based on private ownership just like the political one. The production and the profit gained through the selling of products ensure how the system will prove to be. The economic decisions are made through the operation of a market that is not controlled or regulated by the state. The word traces its origin back to the mid 17th century. It is derived from the word capital which means any monetary assets or something which betters the economic capability and position of any person. It was also used to refer to stocks of merchandise and funds.
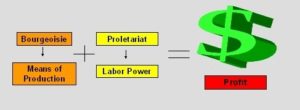
Because capitalism is involved in business activities hence the private company or enterprise is bound to suffer highs and lows. Nothing is certain. The capitalism of any country depends on the global economic changes too.
Types of capitalism:
There are many types of capitalism that differ from country to country and area wise. The commonality between them is that they all involve the process of production and work for a profit. The major types of capitalism are:
- Advanced capitalism
It involves setting up a system in society that will prolong over a period of time. For this, the capitalist model has to be well understood with its complexities and make it well integrated. Antonio Gramsci is considered to be the influencer of advanced capitalism by many writers.
- Finance Capitalism
It is the most important form of capitalism and rules the capitalist society. The financial institutions dominate other stages politically and economically.
- Mercantilism
It is early capitalism in the late 16th century across the nation. It involves national to state business interests, imperialism, etc. In this trade from only within the country was encouraged and expected. Like the colonists who lived in America would purchase goods from their country itself.
- Free- market economy
In this system, the prices of the goods and services on them decided by the people involved in the trade that is of supply and demand. They do so according to their knowledge of what will work in their favor. The government does not interfere or intervene in this decision. Hence the prices are set free.
- State capitalism
As the name suggests the state dominates the capitalist market economy and everything is organized and regulated under the supervision of the state and no one can take independent decisions.
No government interferes in the working of any private working firm. The firms are free to decide whom they want to keep as employees and how much wages should be given. Neither does the government stop any individual from working where he wants to. The government sector and private sectors function separately without interfering in each other’s affairs.
Its staged include:
- Capital accumulation
- Commodity production
- Private ownership
- Existence of good relationship between worker and employee (High wage labour)
- Investment strategies
- Price Mechanism
